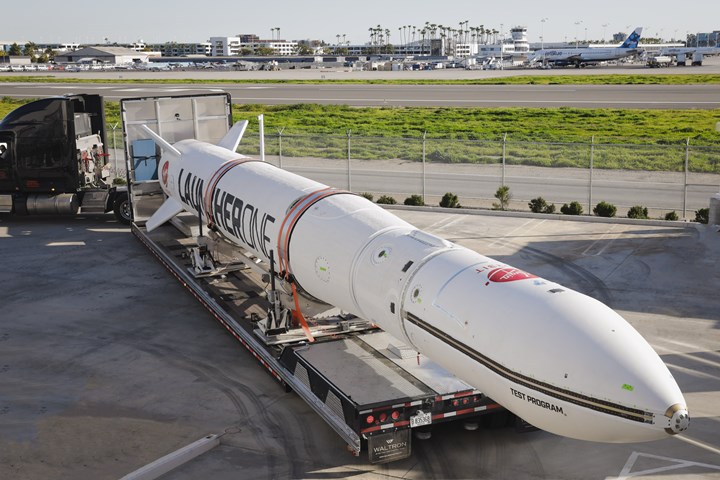
Satellite launch company Virgin Orbit (Long Beach, Calif., U.S.) sent its first successful CubeSat deployer rocket, LauncherOne, into orbit in January 2021 carrying 10 payloads for NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP). LauncherOne, which is deployed via Virgin Orbit’s Cosmic Girl customized 747-400 carrier aircraft, features a carbon fiber composite exterior fuselage and linerless, filament-wound composite propellant tanks.
Following this successful flight, the company is looking to begin ramping up manufacturing operations for LauncherOne satellite deployers at Virgin Orbit’s Long Beach design and manufacturing facility, says Alan Wax, machine shop supervisor at Virgin Orbit. As almost all of the rockets’ components are fabricated and machined in-house, one way the company has been preparing for higher-volume manufacture has been upgrades to the dedicated on-site machine shop. For example, in January 2021 Virgin Orbit finished installation of a customized Multiax America (Grandville, Mich., U.S.) machining center to replace hand trimming and drilling on LauncherOne’s exterior fuselage panels.
“The Virgin Orbit goal is to provide a low-cost ride to space,” Wax explains. “The way to do that is to a) look at labor costs, and b) look at how to automate repetitive processes. The rocket industry is typically infamous for customizing each rocket, for changing things each time they fly. There will be room for iterations and learning and changing as well, but right now what we’re trying to do is get a solid design and production process going, to lower the costs of getting to space.”

Multiax machining center at Virgin Orbit’s facility
As a step toward automating its production process, in 2018, Virgin Orbit began seeking out suppliers for composites machining centers to trim and drill parts ranging in size up to the 24-foot-long carbon fiber prepreg and aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels that make up LauncherOne’s 70-foot fuselage.
Ultimately, Virgin Orbit chose a customized, five-axis high-speed CNC router with a built-in lathe, from Multiax America. According to Joe Bockrath, advanced materials composites automation specialist at Multiax America, once ordered in September 2018, the machine took about a year for design and customization before on-site installation at Virgin Orbit’s facility.
The machine center needed to be able to trim and drill composite components up to 24 feet long, six feet in diameter, and ½-inch thick, Bockrath says, with as much speed and automation as possible while retaining high accuracy. In response, Multiax developed an automated loading system, including two attached, CNC-controlled cranes for loading and unloading parts from the machine. Locating pins are automatically lowered onto the fixtures as well, and locating can be done within a tenth of a millimeter accuracy, Bockrath says. Laser probing has also been installed for higher accuracy. Fixturing for the machine center, Wax notes, was built in-house as well, consisting of an expanding mandrel system to hold the parts in place.
Machining a carbon fiber composite fuselage component for a LauncherOne rocket

Following some installation delays due to COVID-19 and a rigorous inspection process, the machine began operation in January 2021. Overall, the system results in shorter cycle times, higher throughput and less touch labor on LauncherOne’s largest components, Wax says. He notes, “Multiax is very versatile in what they offer, and they were able to take all of our inputs and requirements and needs and really make it work. It’s been great to work with a company that really takes care of us and the machine. Communication and support has been great the entire way.”
As of early June, LauncherOne number five was currently in production. On June 9, Virgin Orbit announced plans to launch its next rocket, carrying seven payloads from the Department of Defense Space Test Program, SatRevolution and the Royal Netherlands Air Force, by the end of June.
Related Content
High-temperature composite 3D printing facilitates design, manufacture of deployable space structures
Opterus R&D employs an AON3D printer and OOA prepregs to build the tooling, prototypes and end-use versions of its foldable CFRP satellite structures.
Read MoreComposite materials, design enable challenging Corvette exterior components
General Motors and partners Premix-Hadlock and Albar cite creative engineering and a move toward pigmented sheet molding compound (SMC) to produce cosmetic components that met strict thermal requirements.
Read MoreRecycling hydrogen tanks to produce automotive structural components
Voith Composites and partners develop recycling solutions for hydrogen storage tanks and manufacturing methods to produce automotive parts from the recycled materials.
Read MoreDesigning an infused, two-piece composite baseball bat
With its Icon BBCOR bat, Rawlings leveraged its experience in braided fabrics and RTM to create an optimized, higher-performance two-piece design.
Read MoreRead Next
Composites in the race to space
Advanced materials use in current and upcoming NASA missions.
Read MoreRocket engine thrust frame proves a strong candidate for composites conversion
The engine thrust frame of a space launch vehicle, located at the bottom of a rocket stage, joining fuel tanks to engines, must deliver strength and stiffness across a range of temperatures — cost-effectively.
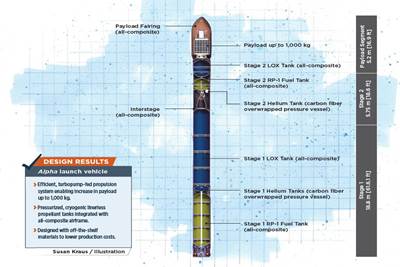
Read MoreThe Alpha launch vehicle: Designing performance in, cost out
Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha 2.0 launch vehicle, designed to deliver satellites into low Earth orbit, gets a composites makeover in pursuit of larger payload capacity and more cost-effective performance.
Read More

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)