AVK announces winners of 2017 Innovation Awards
AVK Industrievereinigung Verstärkte Kunststoffe e.V. (Frankfurt, Germany) has announced the winners of its three prestigious Innovation Awards to institutions, companies and their partners in the composites industry.
AVK Industrievereinigung Verstärkte Kunststoffe e.V. (Frankfurt, Germany) has announced the winners of its three prestigious Innovation Awards to institutions, companies and their partners in the composites industry. All the participating organizations submitted outstanding innovations in the area of fiber reinforced composites. The Innovation Awards were presented during the “3rd International Composites Congress (ICC)” on September 18 and 19 September at the International Congress Center Stuttgart.
The award winners presented their innovations to the international audience during the trade fair. Dr. Elmar Witten, managing director of the AVK, was delighted by the number and quality of the submissions and especially by those of the award winners: “Every year, we are astonished by the level of innovation demonstrated by the research and development departments of companies and institutions in our sector. They are making an important contribution to achieving even greater sustainability and efficiency.”
This year, the jury of leading experts from the sector selected the following award winners:
- In the category “Innovative Products/Applications”: BASF SE (Ludwigshafen, Germany) with its partner company Sonae Arauco (Maia, Portugal) for “3D Mouldable MDF – A new dimension for the furniture industry”
- In the category “Innovative Processes”: Audi AG (Ingolstadt, Germany) and its partner Secar Technology GmbH (Honigsberg, Austria) for “One Shot Technology – A combination of the continuous fiber process and short fiber moulding process for manufacturing exclusive CRP components with a new spectrum of properties.”
- In the category “Research and Science”: Aachen Center for Integrative Lightweight Production (AZL) at RWTH Aachen University (Aachen, Germany) and its partner companies for “Photonics-enabled process chain for manufacturing functionally integrated thermosetting/thermoplastic hybrid components for automobile construction.”
BASF SE has revolutionized the manufacturing process for producing moulded bodies using three-dimensionally mouldable fiberboard. The new binder technology enables manufacturers to make 3D moulded furniture parts cost-efficiently. Industrially manufactured wood products are normally used as panels, e.g. particle board, medium-density fibreboard (MDF), oriented strand board (OSB) or plywood. Until now, curved or moulded parts have rarely been made using these materials. The innovation presented by BASF SE and its partner aims to provide a new wood material for the furniture and interior design industry. The two companies have developed a thermally mouldable composite which can be processed into an intermediate product using existing panel production equipment. This can then be stored for a long period and later moulded into 3D components or stamped with a structured, decorative design. Together with Sonae Arauco, BASF SE has developed a stable MDF panel which can then run through the complete industrial process without the need for additional technical changes to equipment. The major advantage of the product is that it can be moulded simultaneously in all three spatial axes. The simplification of the process and shorter pressing times also increase productivity significantly. The product’s improved moulding properties enable designers to create a wide range of new forms and styles. It can be used to make traditional moulded parts, such as seat shells and backs, as well as deeply structured, bent or curved components. Further applications include, e.g. chairs, door fronts, furniture fronts, room dividers, partition walls for open plan offices, structured floor coverings and panelling for walls or ceilings – here the form can significantly improve room acoustics. It opens a whole new world of opportunities for furniture and interior designers. BASF SE is confident that further research will uncover new applications and unlock the full potential of this material.
The “One Shot Technology” developed by Audi AG directly combines continuous fiber-reinforced profiles with short fiber reinforced moulding material. The component is made without the use of additional adhesive. It enables manufacturers to integrate reinforcement in specific areas to optimize mechanical performance. Areas with the highest properties can now be combined with others featuring significantly reduced properties in a single component. The profiles are manufactured in a pultrusion process and offer outstanding mechanical properties at a moderate cost. The profiles are joined using moulding materials which offer remarkable freedom for designers and the option to integrate further functions.
In addition, the process offers efficiency gains, e.g. by eliminating the need for joining technology. The predicted weight savings compared to metal designs have been proven. The use of the technology in a specific vehicle project has already demonstrated its safety and confirmed the static and dynamic strength of the joins between the profile and the moulding materials. It is ready for use in series production and a type approval certificate is available. The process significantly reduces costs for lightweight construction compared to other fiber composite technologies. Structures manufactured using this technology are typically 15 - 25% lighter than the comparable parts made from aluminum – and 50 - 60% lighter than those made from high strength steel.
Aachen Center for Integrative Lightweight Production (AZL) at RWTH Aachen University and its partner companies BMW AG, KraussMaffei Technologies GmbH, Arges GmbH, Precitec GmbH & Co. KG, Sensortherm GmbH and Zeiss Optotechnik GmbH, have been researching since 2014 the ability to combine thermosetting and thermoplastic FRP using a technique suitable for large series automobile production. The process chain developed by the partners enables manufacturers to produce continuous fiber-reinforced hybrid plastic components for the automotive sector. It is being evaluated using a structural demonstrator component of the BMW i3. The innovation lies in the understanding of the complex interactions between the various parts of the system, the processes and the process parameters as well as the development of the integration solution for the complete manufacturing cell. The ability to combine different plastics in one component opens new possibilities for adapting properties more effectively to the requirements of a specific area of application – e.g. car body components. The entire process chain for the preform right up to quality assurance is integrated into a single manufacturing cell based on an injection moulding machine. The potential savings in material and operating costs throughout the process chain are approx. 20 percent. This new technology can be used to implement new component concepts. For example, BMW has already redesigned part of the structure of the i3. As well as applications in the automobile sector, the technology is also suitable for producing components for other sectors, e.g. mechanical engineering and plant construction, energy and environmental technologies.
Related Content
Hexagon Purus Westminster: Experience, growth, new developments in hydrogen storage
Hexagon Purus scales production of Type 4 composite tanks, discusses growth, recyclability, sensors and carbon fiber supply and sustainability.
Read MoreRecycling end-of-life composite parts: New methods, markets
From infrastructure solutions to consumer products, Polish recycler Anmet and Netherlands-based researchers are developing new methods for repurposing wind turbine blades and other composite parts.
Read MoreBio-based acrylonitrile for carbon fiber manufacture
The quest for a sustainable source of acrylonitrile for carbon fiber manufacture has made the leap from the lab to the market.
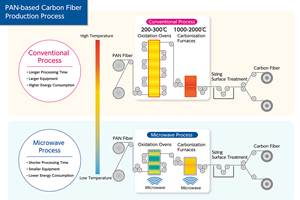
Read MoreMicrowave heating for more sustainable carbon fiber
Skeptics say it won’t work — Osaka-based Microwave Chemical Co. says it already has — and continues to advance its simulation-based technology to slash energy use and emissions in manufacturing.
Read MoreRead Next
All-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read More