Bally Ribbons 3DMAT quartz composite is adopted for future NASA space missions
Named the NASA Government Invention of the Year, the 3D orthogonally woven materials supports structural and thermal performance needs for Orion mission and more.
Bally Ribbon Mills (BRM, Bally, Pa., U.S.), a company that designs, develops and manufactures highly specialized engineered woven fabrics, announces that its 3D orthogonally woven 3DMAT quartz composite materials for the Orion multipurpose crew vehicle (MPCV) compression pads, developed through BRM’s partnership with NASA (Washington, D.C., U.S.), has been named the 2023 NASA Government Invention of the Year. BRM and NASA efforts provide an example of NASA partnering with a small U.S. business to further current and future exploration plans, including the EM-1 lunar mission.
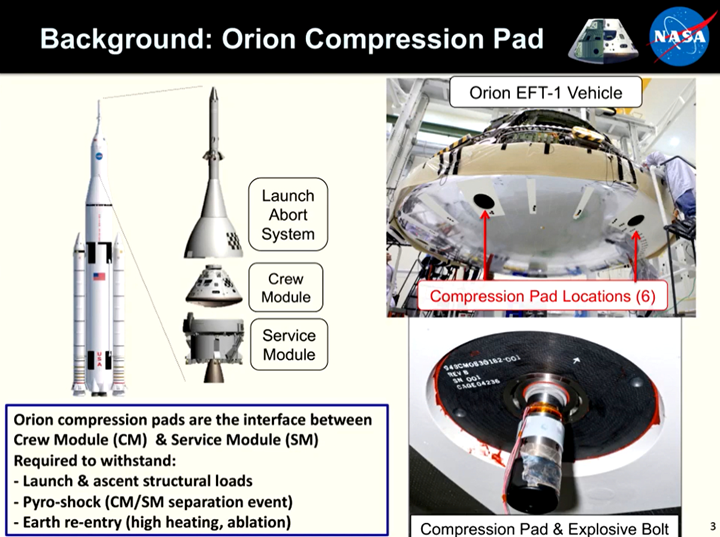
Compression pads serve as the interface between the crew module and service module of the Orion MPCV and carry the structural loads generated during launch, space operation and pyroshock separation of the two modules. The compression pads also serve as an ablative thermal protection system (TPS), withstanding the high heating of Earth reentry.
According to NASA, the initial compression pad design for Orion was complex and limited to Earth orbit return missions, such as the 2014 Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). The 2D carbon fiber-reinforced phenolic material used for EFT-1 has relatively low interlaminar strength and requires a metallic sheer insert to handle structural loads. In general, NASA notes that there are few options for materials that can meet the load demands of lunar return missions due to performance or part size limitations.
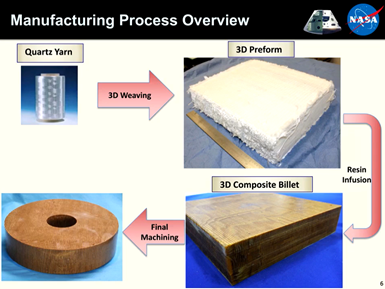
BRM’s 2D- and 3D-woven composite products are constructed from a wide variety of reinforcing fibers and textile forms. The 3D multifunctional ablative thermal protection system (3DMAT) is a woven quartz fiber preform fully densified with cyanate ester resin. It is processed via resin transfer molding (RTM). 3DMAT can be used to produce large composite structures with significant structural capabilities and the ability to withstand high aerothermal heating environments on its outer surface (tested up to 700 watts per cubic centimeter) while keeping the inner surface cool and protected from the aerothermal heating. The robustness of the 3DMAT material is derived from high fiber volume (>56%), 3D-orthoganol architecture and low porosity (0.5%).
Orion has adopted 3DMAT for all future MPCV missions, including EM-1. Additional applications include material handling, aerospace systems, manufacturing and other TPS systems.
For more info on 3DMAT and a webinar on the material, view this link.
Related Content
-
PEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
-
Sulapac introduces Sulapac Flow 1.7 to replace PLA, ABS and PP in FDM, FGF
Available as filament and granules for extrusion, new wood composite matches properties yet is compostable, eliminates microplastics and reduces carbon footprint.
-
Pultrusion: The basics
A primer describing what pultrusion is, its advantages and disadvantages, and typical applications.