NASA’s first flight of Orion with crew may not launch until 2023
It was originally scheduled for 2021, however, after a rigorous technical and programmatic review, the agency announced a new commitment to be ready for a launch with astronauts no later than April 2023.
Share
NASA's Orion spacecraft, which will send astronauts to deep space destinations where no other human has traveled, could be delayed two years, until 2023. It was originally scheduled for 2021, however, after a rigorous technical and programmatic review, the agency announced a new commitment of April 2023.
“Our work to send humans out into the solar system is progressing,” said NASA Administrator Charles Bolden. “Orion is a key piece of the flexible architecture that will enable humanity to set foot on the Red Planet, and we are committed to building the spacecraft and other elements necessary to make this a reality.”
A successful test of an uncrewed Orion capsule, Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1), flew in December 2014, providing important data that allowed engineers to identify risks associated with deep space flight and re-entry and use that knowledge to improve the design of Orion for its next test flights, Exploration Missions 1 and 2 (EM-1 and EM-2). The flight tested Orion’s composites heat shield, avionics, parachutes, computers and key spacecraft separation events, exercising many of the systems critical to the safety of astronauts who will travel in Orion.
Performance data has helped to improve manufacturing processes, as well. Engineers have already incorporated many of these improvements into elements of the EM-1 design, including the crew compartment or pressure vessel, which now is in fabrication and assembly at companies across the country. The vessel is comprised of seven panels or sections, and the first two of these were welded together earlier in September. When complete, this capsule will launch on NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the first fully integrated flight test, EM-1.
Astronauts will fly on Orion for the first time on EM-2. That mission will build on the results of the EM-1 flight with additional requirements that the Orion capsule includes fully integrated environmental control and life support systems; controls; and communications designed specifically for the human operation; and advanced launch and re-entry spacesuits for the crew. The recent review, culminating in what is known within NASA as Key Decision Point C (KDP-C), includes all of these technological advancements, and approval represents agency support for this work and the Orion program plan.
The decision commits NASA to a development cost baseline of $6.77 billion from October 2015 through the first crewed mission (EM-2) and a commitment to be ready for a launch with astronauts no later than April 2023. The commitment is consistent with funding levels in the president’s budget request. Conservative cost and schedule commitments outlined in the KDP-C align the Orion Program with program management best practices that account for potential technical risks and budgetary uncertainty beyond the program's control.
“As we take these steps to develop the capabilities we need to send astronauts deep into space, we’re also aligning how we manage our human exploration systems development programs to ensure we are prepared for unforeseen future hurdles,” said Robert Lightfoot, NASA associate administrator. “We’re committing to this funding and readiness level to stay on the journey we’ve outlined to get to Mars.”
Orion engineers now are executing a rigorous review of the spacecraft’s engineering design and technical progress of the vehicle systems and subsystems. This critical design review (CDR) will demonstrate Orion is ready to proceed to full-scale fabrication, assembly, integration and testing. NASA’s SLS Program recently completed this milestone, and its Ground Systems Development and Operations (GSDO) Program will begin its review this fall.
“The Orion Program has done incredible work, progressing every day and meeting milestones to prepare for our next missions,” said William Gerstenmaier, the agency’s associate administrator for Human Exploration and Operations at NASA Headquarters. “The team will keep working toward an earlier readiness date for a first crewed flight, but will be ready no later than April 2023, and we will keep the spacecraft, rocket and ground systems moving at their own best possible paces.”
In the coming months, Orion will complete its CDR; see the arrival of a test version for the European Space Agency-provided service module at NASA’s Plum Brook Station near Sandusky, Ohio; perform a series of parachute tests; and complete the welding of the crew pressure vessel. Although Orion’s readiness date for EM-1 was not formally part of the KDP-C milestone commitment, engineers continue to work toward a commitment for SLS and GSDO to be ready for the uncrewed mission in fall 2018, and NASA will set an integrated launch date after GSDO’s critical design review is completed.
Related Content
Plant tour: Arris Composites, Berkeley, Calif., U.S.
The creator of Additive Molding is leveraging automation and thermoplastics to provide high-volume, high-quality, sustainable composites manufacturing services.
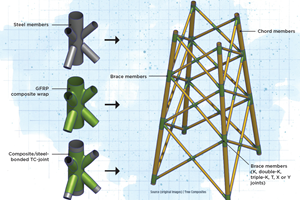
Read MoreNovel composite technology replaces welded joints in tubular structures
The Tree Composites TC-joint replaces traditional welding in jacket foundations for offshore wind turbine generator applications, advancing the world’s quest for fast, sustainable energy deployment.
Read MoreRecycling hydrogen tanks to produce automotive structural components
Voith Composites and partners develop recycling solutions for hydrogen storage tanks and manufacturing methods to produce automotive parts from the recycled materials.
Read MoreNatural fiber composites: Growing to fit sustainability needs
Led by global and industry-wide sustainability goals, commercial interest in flax and hemp fiber-reinforced composites grows into higher-performance, higher-volume applications.
Read MoreRead Next
VIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read More