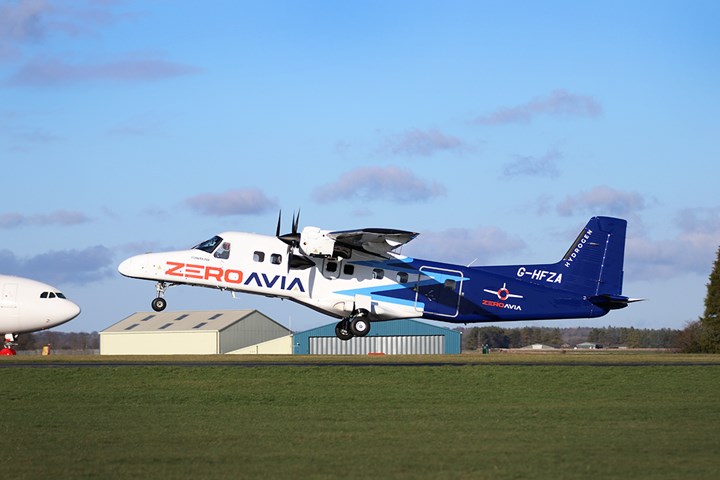
ZeroAvia successfully flies hydrogen-electric Dornier 228 testbed aircraft
The 19-seat twin-engine aircraft took to the skies for the first time as part of the HyFlyer II project, moving ZeroAvia toward its 2025 targets and scaling the technology to larger airframes.
On Jan. 19 ZeroAvia (Kemble, U.K.) flew what the company claims to be the largest aircraft in the world to be powered by a hydrogen-electric engine. The zero-emission aviation company took to the skies for the maiden flight of its 19-seat Dornier 228 testbed aircraft, retrofitted with a full-size prototype hydrogen-electric powertrain on the left wing of the aircraft.
The flight took place from the company’s R&D facility at Cotswold Airport in Gloucestershire, U.K., and lasted 10 minutes. At 1:35 p.m. GMT the aircraft completed taxi, takeoff, a full pattern circuit and landing. The landmark flight forms part of the HyFlyer II project, a major R&D program backed by the UK government’s flagship ATI Program, which targets development of a 600-kilowatt powertrain to support 9-19 seat aircraft worldwide with zero-emission flight.
The twin-engine aircraft was retrofitted to incorporate ZeroAvia’s hydrogen-electric engine on its left wing, which then operated alongside a single Honeywell TPE-331 stock engine on the right. In this testing configuration, the hydrogen-electric powertrain comprises two fuel cell stacks, with lithium-ion battery packs providing peak power support during takeoff and adding additional redundancy for safe testing. In this testbed configuration, hydrogen tanks and fuel cell power generation systems were housed inside the cabin. In a commercial configuration, external storage would be used and the seats restored.
“This is a major moment … as it shows that true zero-emission commercial flight is only a few years away.”
All systems performed as expected. This is the largest ZeroAvia engine tested to date, and places the company on the direct path to a certifiable configuration to be finalized and submitted for certification in 2023, with this program also serving as key to unlocking speedy technology development for larger aircraft. ZeroAvia’s 2-5-megawatt powertrain program, already underway, will scale the clean engine technology for up to 90-seat aircraft, with further expansion into narrowbody aircraft demonstrators over the next decade.
Of note, this flight test campaign is being conducted under a full Part 21 flight permit with the U.K. CAA, which is a much more stringent set of requirements compared to the E-Conditions framework ZeroAvia used for its six-seat prototype test flights in the prior years. This signifies the maturity of the company’s processes and design approaches and its readiness to proceed towards full commercial certification of its powerplants.
ZeroAvia says it will now work towards its certifiable configuration in order to deliver commercial routes using the technology by 2025. The Dornier 228 will conduct a series of test flights from Kemble and later demonstration flights from other airports. Almost exactly two years ago, ZeroAvia conducted the first of more than 30 flights of a six-seat Piper Malibu aircraft using a 250-kilowatt hydrogen-electric powertrain.
“This is a major moment, not just for ZeroAvia, but for the aviation industry as a whole, as it shows that true zero-emission commercial flight is only a few years away,” Val Miftakhov, founder and CEO of ZeroAvia, says. “The first flight of our 19-seat aircraft shows just how scalable our technology is and highlights the rapid progress of zero-emission propulsion.”
This latest achievement follows ZeroAvia’s previous milestones, starting with six-seat prototype flights of a Piper M-Class airframe in 2019, and the commercial-scale six-seater hydrogen-electric powered flight in September 2020. The 2020 prototype was a part of the HyFlyer I program in the U.K. Unlike the previous tech demonstrator program, ZeroAvia’s 600-kilowatt engine being developed under HyFlyer II is a commercial-intent program.
The hydrogen-electric powertrain on board was fueled using compressed gaseous hydrogen produced with an on-site electrolyzer. To enable hydrogen production on site, ZeroAvia and HyFlyer II partner the European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC, Stromness, Scotland) have delivered and operated the Hydrogen Airport Refueling Ecosystem (HARE), a microcosm of what infrastructure will look like in terms of green hydrogen production, storage, refueling and fuel cell powered flight. The system’s electrolyzer capacity was doubled earlier this year from its initial design for the latest project.
ZeroAvia’s HyFlyer II program to develop its ZA-600 hydrogen-electric engine and retrofit the Dornier 228 is being delivered in partnership with EMEC and Aeristech (Warwick, U.K.) and is supported by the UK government through the ATI Program and the Department for Business, Energy Industrial Strategy, Innovate UK and Aerospace Technology Institute (ATI). Val Miftakhov is also a member of the UK government’s Jet Zero Council.
For more information on how ZeroAvia is making strides, not only in zero-emissions flight, but composites, see “ZeroAvia advances to certify ZA600 in 2025, launch ZA2000 with liquid hydrogen in 2027.”
Related Content
Infinite Composites: Type V tanks for space, hydrogen, automotive and more
After a decade of proving its linerless, weight-saving composite tanks with NASA and more than 30 aerospace companies, this CryoSphere pioneer is scaling for growth in commercial space and sustainable transportation on Earth.
Read MorePlant tour: Middle River Aerostructure Systems, Baltimore, Md., U.S.
The historic Martin Aircraft factory is advancing digitized automation for more sustainable production of composite aerostructures.
Read MoreASCEND program update: Designing next-gen, high-rate auto and aerospace composites
GKN Aerospace, McLaren Automotive and U.K.-based partners share goals and progress aiming at high-rate, Industry 4.0-enabled, sustainable materials and processes.
Read MoreCryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreRead Next
NASA picks Boeing’s Transonic Truss-Based Wing for Sustainable Flight Demonstrator project
With the help of NASA, Boeing will build, test and fly a full-scale demonstrator aircraft starting in 2028, gearing toward a greener, more fuel-efficient future aircraft.
Read MoreAirbus reveals hydrogen-powered zero-emission engine
Fuel cell engine architecture will be tested onboard Airbus’ ZEROe demonstrator aircraft to determine feasibility of a 2035 entry-into-service.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read More