CAMX 2022 exhibit preview: Boston Materials
Bimetal is an engineered carbon fiber metal laminate that offers a different solution to monolithic sheet metals. Bimetal is said to have good mechanical properties and be lighter to traditional monolithic materials.
Bimetal, from Boston Materials Inc. (Boston, Mass., U.S.), is an engineered carbon fiber metal laminate (FML). The carbon fiber in the composite is positioned vertically in the Z-axis as opposed to horizontal, unidirectional (UD) carbon fiber. Sandwiched between two metal layers, Boston Materials says Bimetal positions itself as a viable solution to replace monolithic sheet metals.
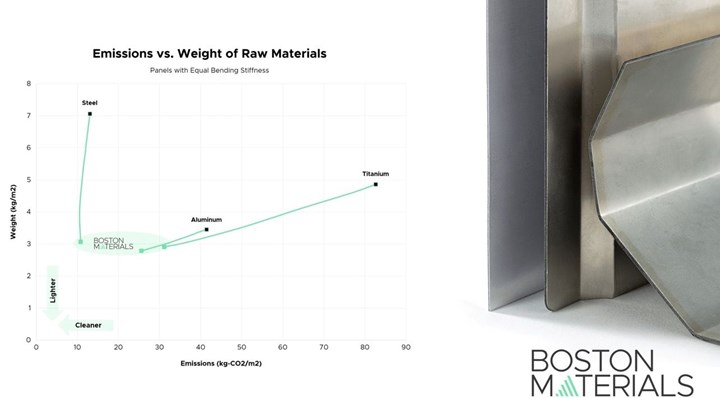
With lightweighting becoming a major focus for reducing emissions, there is a need to develop scalable, affordable technologies to reduce weight and improve performance. FMLs like Bimetal are known for having good mechanical properties and being lighter than traditional monolithic materials, the company notes. The benefits of combining two materials to produce structures to outperform individual counterparts on weight and performance highlights the need for developing more efficient alternatives than monolithic materials.
Boston Materials’ Z-axis carbon fiber (Dry ZRT) is able to combine with various thermoplastics or thermosets to create a Z-axis carbon fiber composite that can be tailored to a customer’s needs. The ZRT composite’s strength works much like an I-Beam within the Bimetal structure. The core Z-axis carbon fibers (ZRT) represent the vertical element and the metal layers represent the face and flange, working together to create a higher shear strength, impact resistance and tuned flexural rigidity.
Bimetal panels are a high strength, lightweight material that provides efficient mechanical performance, increased impact resistance and tailored flexural rigidity, according to Boston Materials. Its Bimetal panels are a suitable alternative to monolithic materials as well as traditional core materials, such as plywood, balsa and foam.
The panels are available in a wide range of sheet sizes and are designed for ease of use in many common applications and processes. Boston Materials says the panels can be engineered to meet specific requirements for strength and stiffness while also being suitable for water cutting, laser welding, forming, stamping and, in some cases, plasma cutting. Applications include, but are not limited to, building products, commercial products, ground transportation, marine and recreation and electronics box-builds.
Related Content
-
Carbon fiber, bionic design achieve peak performance in race-ready production vehicle
Porsche worked with Action Composites to design and manufacture an innovative carbon fiber safety cage option to lightweight one of its series race vehicles, built in a one-shot compression molding process.
-
Jeep all-composite roof receivers achieve steel performance at low mass
Ultrashort carbon fiber/PPA replaces steel on rooftop brackets to hold Jeep soft tops, hardtops.
-
Bio-based acrylonitrile for carbon fiber manufacture
The quest for a sustainable source of acrylonitrile for carbon fiber manufacture has made the leap from the lab to the market.