Covestro introduces 3D printing material made from recycled PET
Glass fiber-filled rPET suitable for high performance and structural applications using 3D pellet printing/fused granulate fabrication (FGF).
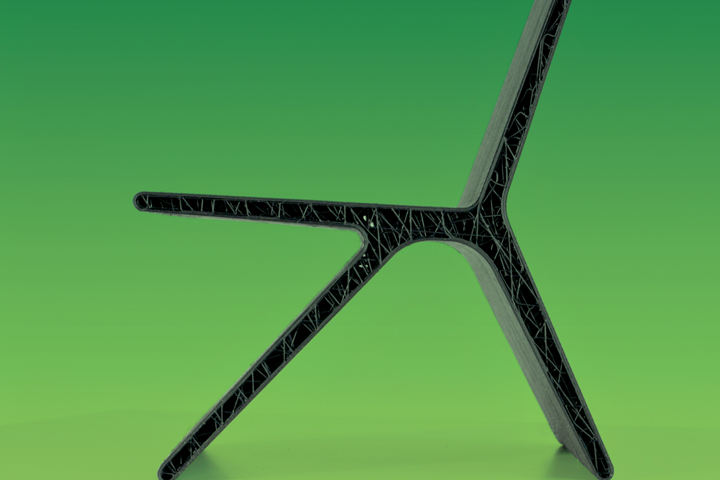
Covestro’s glass-filled rPET material can be used to make, for example, furniture such as this chair, designed by Michiel van der Kley. Photo Credit: Covestro AG
Materials manufacturer Covestro (Leverkusen, Germany) introduces its first material developed by the additive manufacturing (AM) business recently acquired from Royal DSM (Geleen, Netherlands): a glass-fiber filled recycled polyethylene terephthalate (rPET) for 3D pellet printing. Made from post-consumer PET waste, Arnite AM2001 GF (G) rPET brings structural performance to a part at a substantially lower carbon footprint than virgin material, enabling manufacturers to achieve a more circular supply chain without the need to compromise on performance.
Covestro says this technology, also known as fused granulate fabrication (FGF), permits fast and economically viable additive manufacturing of large-size parts. Direct printing of applications lowers cost by reducing product development time, and 3D printing ensures design flexibility, which can help reduce material cost.
Arnite AM2001 (G) rPET’s mechanical properties and broad processing window makes it ideally suited for structural applications across a variety of industries, including pedestrian bridges, tiles for cyclist or pedestrian tunnels, architectural applications like cladding or partition walls, in- and outdoor furniture, small boats, packaging crates or tooling.
Related Content
-
Plant tour: Spirit AeroSystems, Belfast, Northern Ireland, U.K.
Purpose-built facility employs resin transfer infusion (RTI) and assembly technology to manufacture today’s composite A220 wings, and prepares for future new programs and production ramp-ups.
-
Sulapac introduces Sulapac Flow 1.7 to replace PLA, ABS and PP in FDM, FGF
Available as filament and granules for extrusion, new wood composite matches properties yet is compostable, eliminates microplastics and reduces carbon footprint.
-
The next evolution in AFP
Automated fiber placement develops into more compact, flexible, modular and digitized systems with multi-material and process capabilities.













