CarbonPro box: new forming process
From materials to assembly, the carbon fiber composite CarbonPro box manufacturing process features innovative, automated preforming technologies.
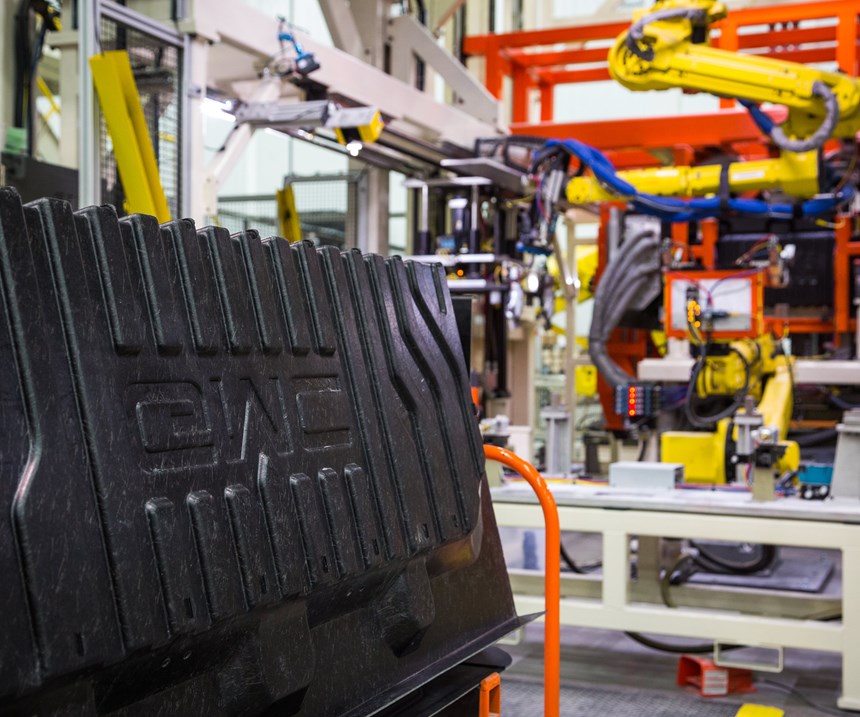
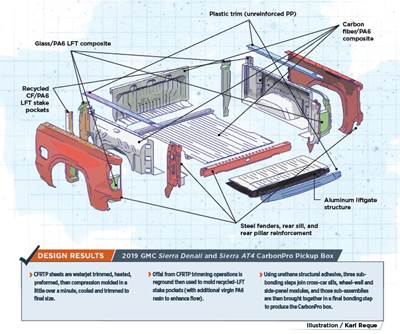
With the new and innovative design of the carbon fiber composite CarbonPro pickup box comes a new manufacturing process (see more about its design and development in “Chopped carbon fiber, polyamide and innovation redefine the modern pickup truck bed”). Starting with preforming at a Continental Structural Plastics’s Huntington plant (CSP; Huntington, Ind., U.S.) and finishing with pickup assembly at the Fort Wayne Assembly plant of General Motors Co. (GM; Roanoke, Ind., U.S.), here’s what we know.
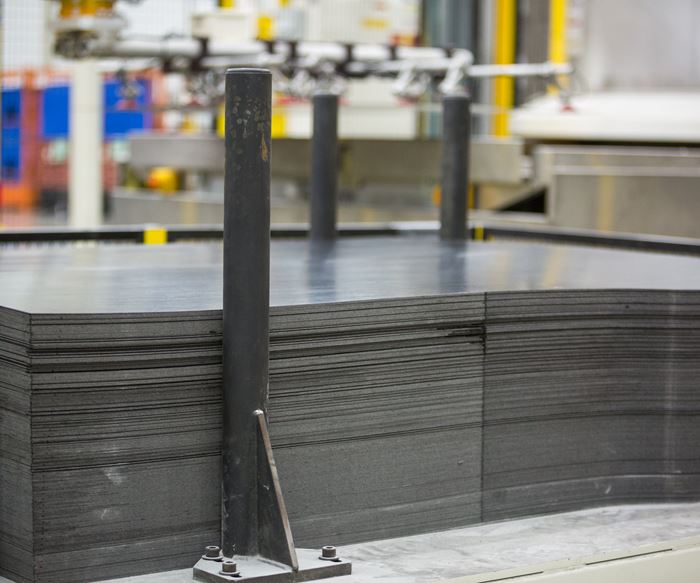
The process of converting 2D sheets to 2.5D/3D parts begins with waterjet cutting of Teijin Ltd.’s (Tokyo, Japan) Sereebo carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composite (CFRTP) sheets to a near-net shape (See Steps 1 and 2 of the manufacturing process at CSP above; equipment from Shape Process Automation, Auburn Hills, Mich., U.S.).
Next, robots load trimmed sheets into a hot-air oven beside the press (Steps 3 and 4). What will become the A-surface is placed face-down; a much-smaller “patch layer” is placed in a key location requiring greater thickness/higher mechanical performance on what will be the B-side of the part. Multiple sheets of material move through the oven as temperatures are gradually increased above PA6’s glass-transition temperature (Tg) but well below its typical melt temperature for reinforced grades. Keeping the heat-soak lower and slower helps prevent damage to the matrix, protects the UV additive package and reduces resin flow during molding to preserve isotropy.
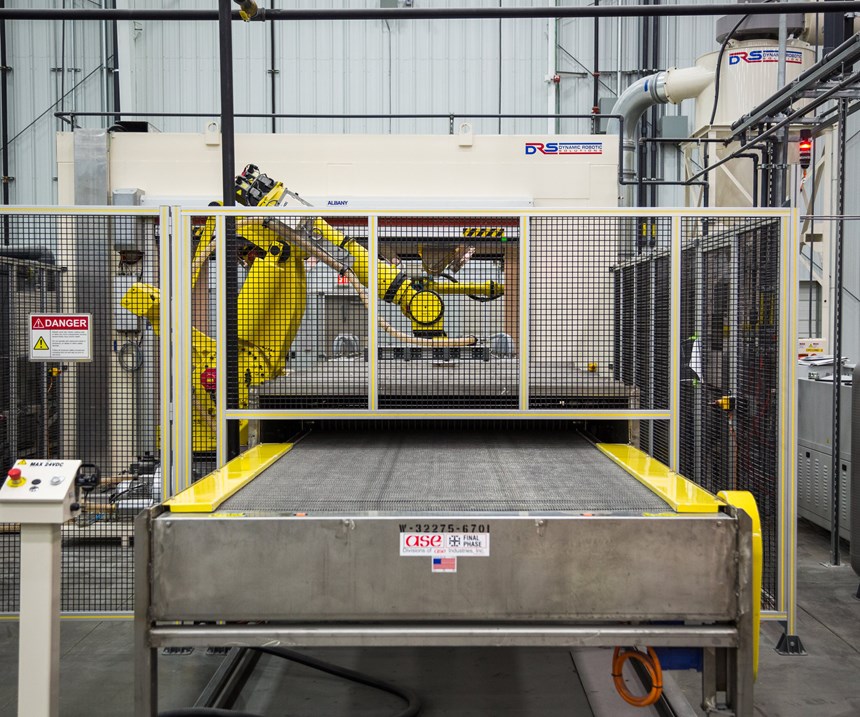
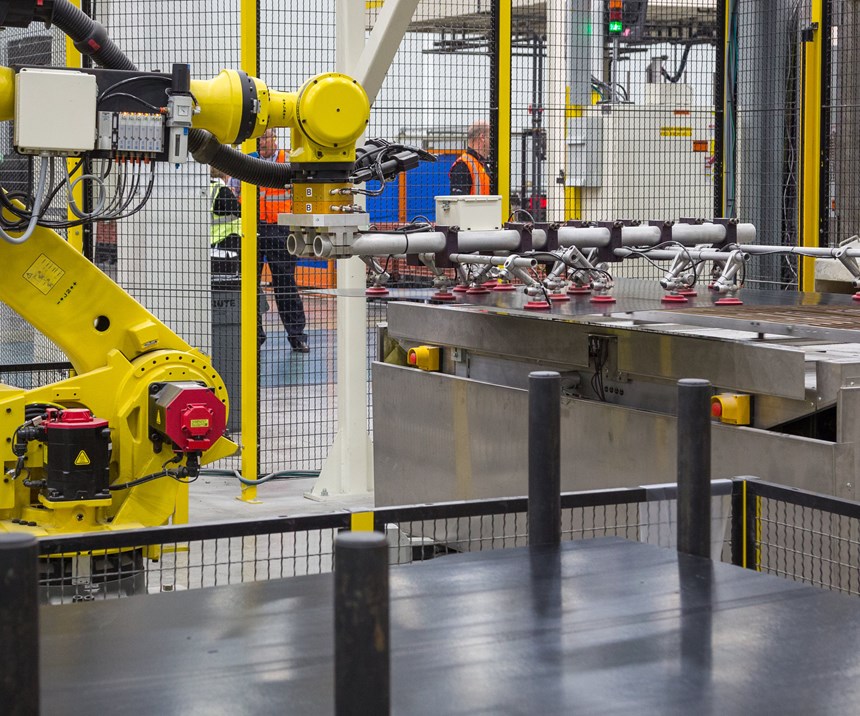
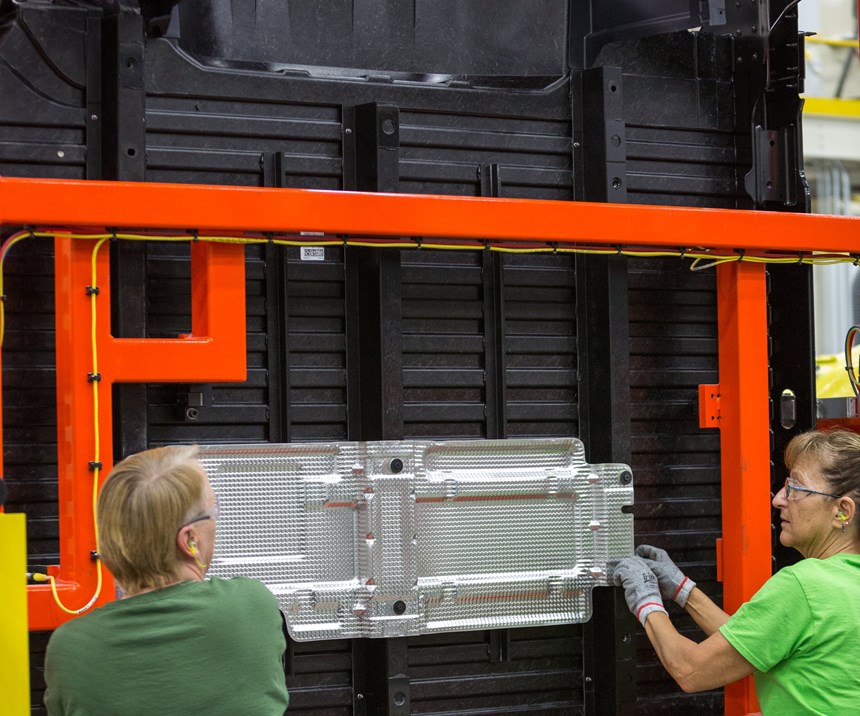
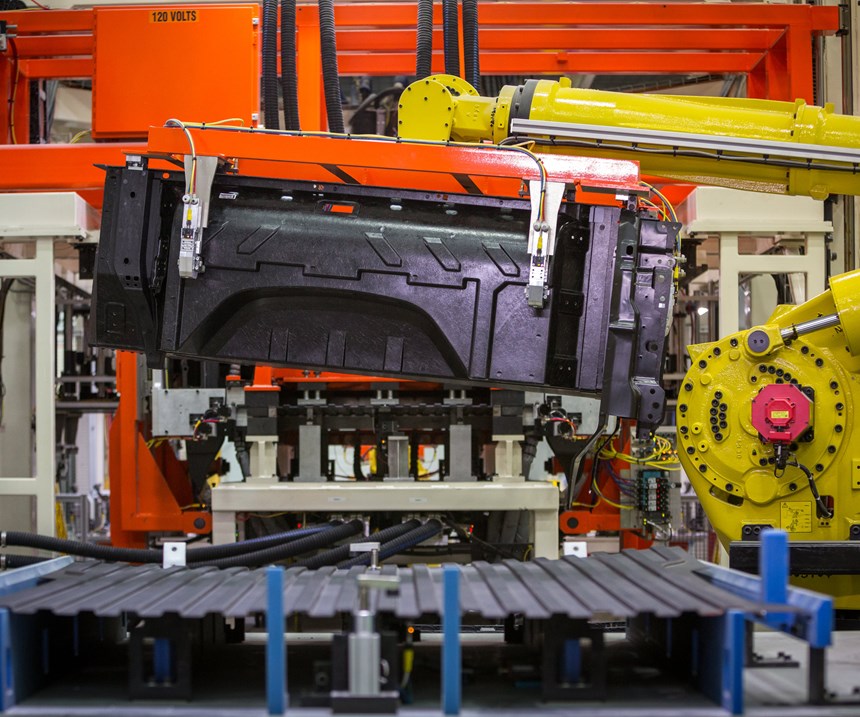
Once the pair of blanks (now fused into a single sheet) exit the oven, a robot (from FANUC America Corp., Rochester Hills, Mich., U.S.) picks up the hot material with needle grippers and conveys it the short distance from oven to press, which is open and whose last part has just been unloaded (Step 4). Once over the press, the sheet is preformed, then carefully tucked into the core side of the heated tool. The press closes, material is formed and quenched, the press opens and the part is demolded and cools on a conveyor (no special fixtures required; Step 5). Reportedly, the complete cycle time (from oven transfer to demolding) is slightly more than 1 minute — a critical target assuring the process is fast enough to supply medium-to-high production volumes in the auto industry.
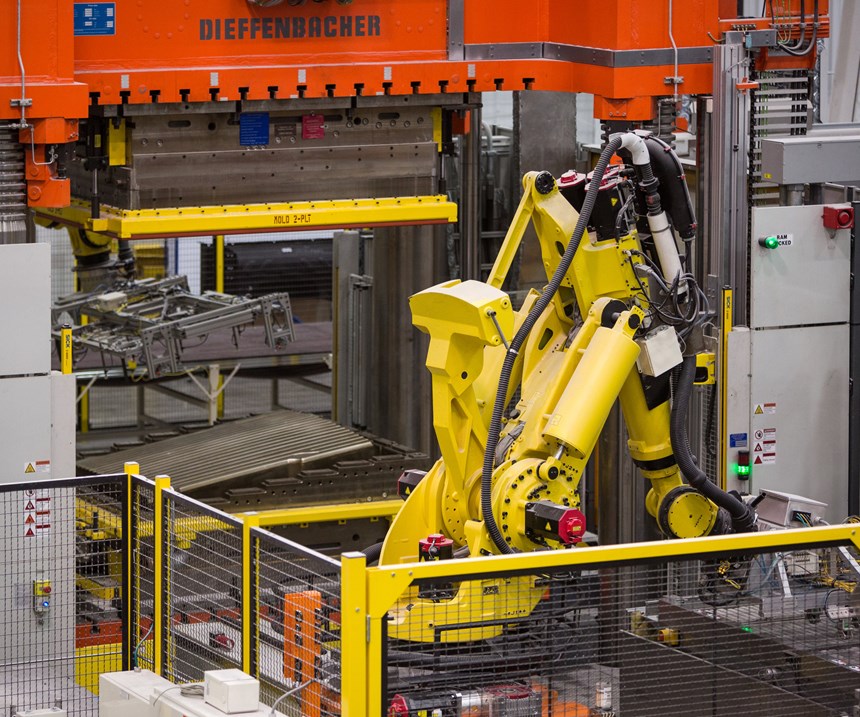
The four largest CarbonPro parts are molded on an innovative new 3,600-metric ton press with a 3,600-by-2,500-millimeter platen from Dieffenbacher GmbH (Eppingen, Germany). This press is capable of 5-second open/close cycles that are more akin to metal stamping than typical composites molding. Interestingly, the press does not mold on stops as with conventional compression molding, although reportedly it can be used to mold glass mat thermoplastics (GMT), direct long fiber thermoplastics (D-LFT) and sheet molding compound (SMC) as well as Sereebo.
Tooling is said to be conventional P20 steel and uses “open” shear edges, since material doesn’t really flow. Instead, oversized parts are pressed and subsequently trimmed to final size during post-mold finishing. Tools for the CarbonPro box were supplied by Paragon D&E of Wixom, Mich., U.S., and WM Tool Inc. of Winsor, Ontario, Canada. Mark Voss, engineering group manager of advanced structural composites and pickup boxes at General Motors Co., reports that there are no fancy features on these tools. However, the biggest challenge with both part and tool design was anticipating warpage on such big parts and designing tooling to accommodate this. Pelczarski notes that the toughest CarbonPro parts to mold are the side panels, owing to all their geometry. “To get things just right required significant work,” he adds.
An innovative feature of the whole system is how fast tool changes can be made, as both press and robot tooling are changed every time CSP completes a run of one CarbonPro part and prepares to run another. Preheating stations are located on either side of the press and are joined via a shuttle system. When one tool is in the press, another sits in one of the preheating stations. When the production run is completed, the shuttle moves the current tool out of the press and off to the other preheating station and slides the tool that’s been waiting into the press. Quick connect/disconnect features facilitate rapid changeover. GM claims tool changeover on the Dieffenbacher press takes less than five minutes.
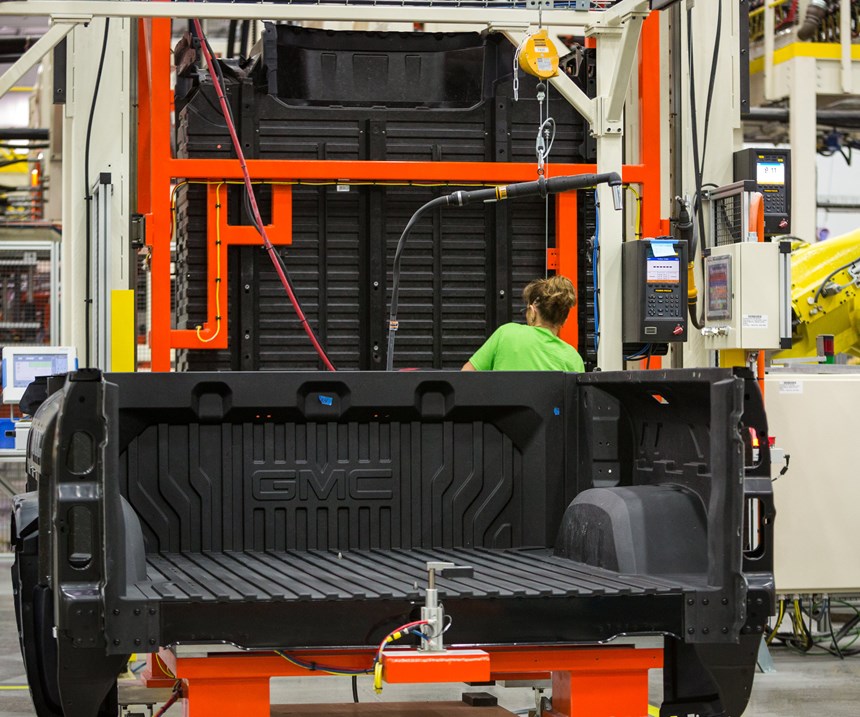
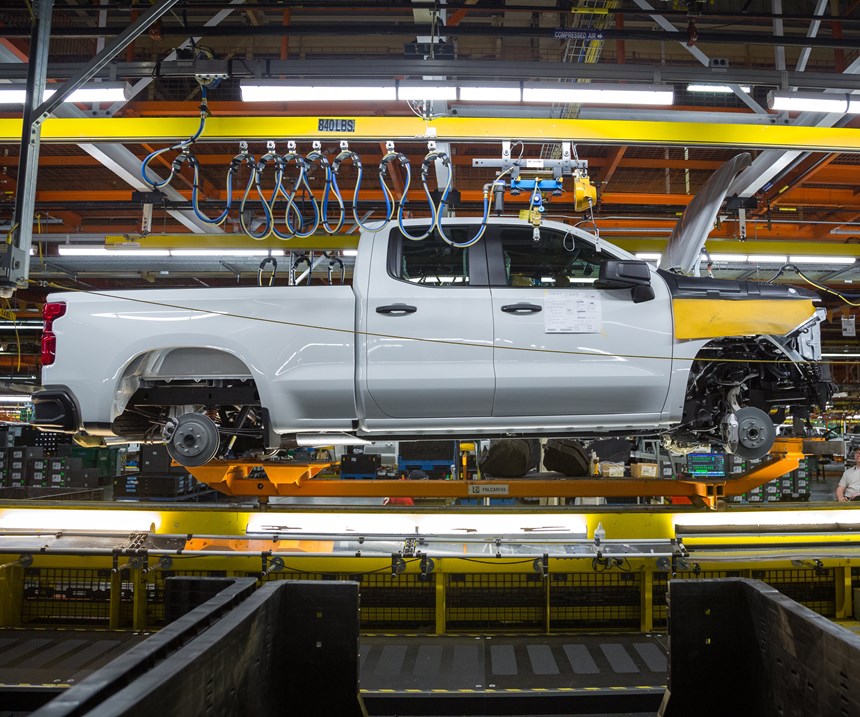
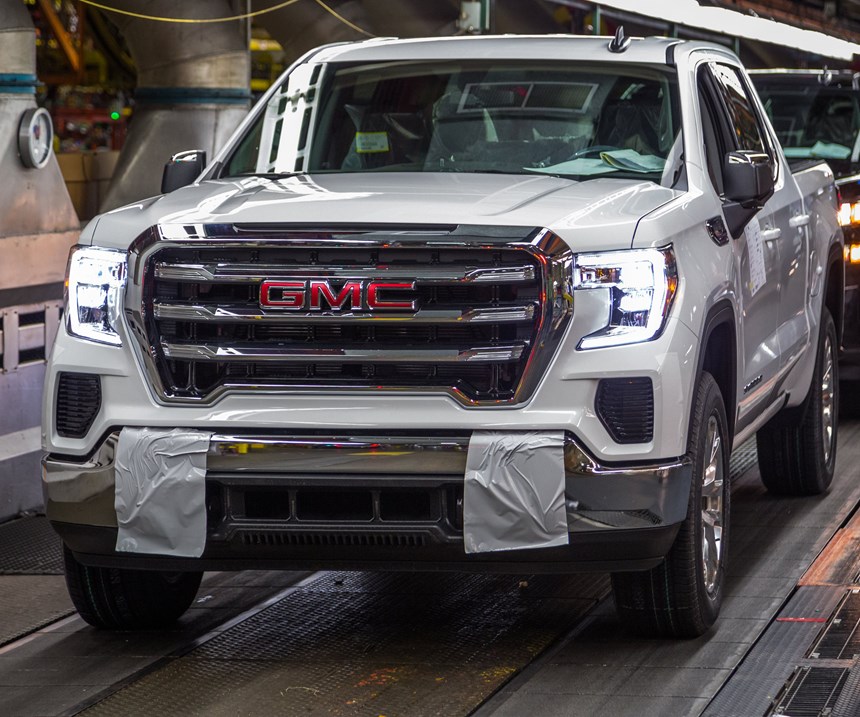
Assembled CarbonPro boxes (Steps 7 and 8) are shipped to GM’s plant for final assembly on select GMC Sierra AT4 (offroad) and Denali models (Steps 9-11).
Related Content
Plant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MoreRecycling hydrogen tanks to produce automotive structural components
Voith Composites and partners develop recycling solutions for hydrogen storage tanks and manufacturing methods to produce automotive parts from the recycled materials.
Read MoreTPI manufactures all-composite Kenworth SuperTruck 2 cab
Class 8 diesel truck, now with a 20% lighter cab, achieves 136% freight efficiency improvement.
Read MoreCarbon fiber, bionic design achieve peak performance in race-ready production vehicle
Porsche worked with Action Composites to design and manufacture an innovative carbon fiber safety cage option to lightweight one of its series race vehicles, built in a one-shot compression molding process.
Read MoreRead Next
Chopped carbon fiber, polyamide and innovation redefine the modern pickup truck bed
CarbonPro, the first thermoplastic composite box, boosts damage resistance, reduces mass 28 kg, scales to high production volumes.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)