Move over honeycomb, thermoplastic sandwich is commercialized as DYNATECH
PEI foam core/skin sandwich panels claim to save up to 40 percent weight and 30 percent cost in rail and aircraft interiors vs. honeycomb.

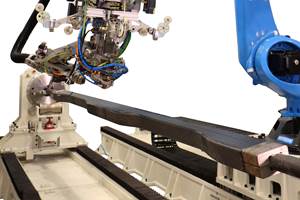
SMTC has launched DYNATECH thermoplastic sandwich panels for transportation interiors based on FITS technology. SOURCE: SMTC
Honeycomb-cored sandwich panels have been used in aircraft interiors since the 1970s. Passenger rail is more conservative and cost-sensitive, but in Europe, aluminum-cored composite panels have become fairly common. Fiberglass-faced (aircraft and rail) or metal-faced (rail) honeycomb is used in baggage bins (stowbins), lavatories, galleys, tables, trays, partitions, doors and trolley carts. Compression molded cored panels are also used in shaped sidewall and overhead panels. Sara Black’s 2006 CT article, “Advanced materials for aircraft interiors” is a good primer on standard materials and processes used.
A new material has been launched for this market by SMTC (Bouffere, France), a manufacturer of transportation interiors using composite panels since 1983. The company announced at JEC Europe 2014 its launch of DYNATECH thermoplastic sandwich panels, based on its acquisition of Foamed In-situ Thermoformable Sandwich technology from FITS Technology (Driebergen, The Netherlands) inventor and CEO, Martin de Groot (see my article “Thermoformable Composite Panels, Part II” in CT June 2006).

FITS technology was developed to reduce weight and cost in aircraft and other transport interiors. SOURCE: Fits Technology
DYNATECH encompasses an automated panel-making process that enables polyetherimide (PEI) to be in-situ foamed as a core (with a vertical cell structure) and then receive fiber-reinforced PEI skins that are “welded” onto the core inline, as both are thermoplastic. This thermoplastic panel stock is then easily thermoformed into shapes and angles, edges are easily sealed and inserts do not require potting. FITS inventor de Groot asserts that 25 percent of a Nomex honeycomb panel’s weight comes from potting, exterior decorative layers (e.g., Declar) and connections.


DYNATECH panels reportedly offer weight and labor savings via automated processes for thermoformed edges and fastener installation. SOURCE: FITS Technology
The concept of a lightweight cored panel made using a belt press and reinforced thermoplastic faceskins was patented by DuPont in 1990 based on its polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) polymer. CW reported on Fokker’s use of carbon fiber/PEI skins on Nomex honeycomb for the G650 load floors (see “Thermoplastic composites: Inside story”, in HPC Feb 2009). And SABIC (Pittsfield, Mass., USA) has been marketing its Ultem PEI foam for applications like aircraft baggage bins since 2008.
What makes DYNATECH different is that all of the pieces have been put together, including core, skins, thermoforming shapes, edge-finishing, insert installation and now automated panel manufacturing through SMTC’s commercialization of the product. Also, SMTC is an established supplier of interiors, with customers like Bombardier, Alstom, Sogerma and Zodiac Aerospace. Hence, it knows the cost and performance targets and already has supplier relationships in place. Interestingly, a representative from interiors giant Zodiac Aerospace was at the JEC Europe 2014 press conference, and SMTC said it has already discussed qualification with several OEMs.
I’ve asked de Groot for test data showing the reported acoustic and thermal insulation benefits of DYNATECH vs. honeycomb-cored panels, and also for the calculations used to assert the 20 to 40 percent weight savings and 10 to 30 percent cost savings possible. The PEI foam core is higher in density than Nomex honeycomb, but SMTC and de Groot are claiming the structures can be made much thinner. That alone is intriguing as airlines and OEMs look for more interior space.
Also, the big topic at Airbus and Boeing now is “multifunctional,” where interior structure is integrated with other functions such as ventilation, lighting, electrical power, etc., into walls, ceilings and bins. It might be possible to embed a variety of structural components and/or functional elements (e.g., fiber optics) within DYNATECH's core. De Groot also claims that unique design advantages can be exploited — for example, a box-type reinforcement achieved from folding and thermoforming skins up around the panel edges and welded or thermoformed local reinforcements.
The FITS Technology website features a page of videos demonstrating the concepts for automated edge finishing and insert installation. Illustrations for corner and edge reinforcements are also shown.
SMTC says pilot production will begin this summer with high-volume production slated for 2016.
Related Content
JEC World 2024 highlights: Thermoplastic composites, CMC and novel processes
CW senior technical editor Ginger Gardiner discusses some of the developments and demonstrators shown at the industry’s largest composites exhibition and conference.
Read MoreMFFD thermoplastic floor beams — OOA consolidation for next-gen TPC aerostructures
GKN Fokker and Mikrosam develop AFP for the Multifunctional Fuselage Demonstrator’s floor beams and OOA consolidation of 6-meter spars for TPC rudders, elevators and tails.
Read MoreManufacturing the MFFD thermoplastic composite fuselage
Demonstrator’s upper, lower shells and assembly prove materials and new processes for lighter, cheaper and more sustainable high-rate future aircraft.
Read MorePlant tour: Albany Engineered Composites, Rochester, N.H., U.S.
Efficient, high-quality, well-controlled composites manufacturing at volume is the mantra for this 3D weaving specialist.
Read MoreRead Next
VIDEO: High-rate composites production for aerospace
Westlake Epoxy’s process on display at CAMX 2024 reduces cycle time from hours to just 15 minutes.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read MorePlant tour: A&P, Cincinnati, OH
A&P has made a name for itself as a braider, but the depth and breadth of its technical aptitude comes into sharp focus with a peek behind usually closed doors.
Read More