New 250°F/120°C No Oven No Autoclave epoxy
Designed for room-temp infusion and filament winding with 2-hr no-heat-added cure or 15-30 min heated cure without post-cure for flexible processing of marine, industrial and energy structures.

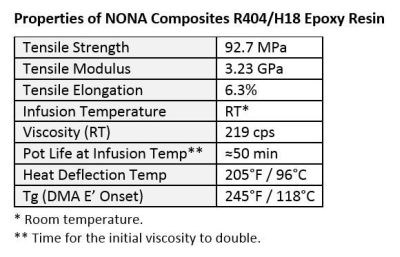
New NONA R404/H18 epoxy resin offers curing and tooling flexibility for a wide range of structures, including large marine infusions and filament wound tanks for energy applications. SOURCE: NONA Composites.
NONA Composites (Dayton, OH, US) will unveil its new R404/H18 resin system at CAMX 2015 (Oct. 26-29, Dallas, TX, US). This new epoxy resin enables room temperature infusion or filament winding followed by a relatively fast (≈ 2-hr) cure without adding any heat (i.e., no oven no autoclave) or an even faster (15-30 min) heat-added cure (250°F/120°C) with no post-cure, to enable faster, larger, and more flexible composite processing for filament wound pressure vessels, marine structures, industrial composites, and even some lower-temperature aerospace composites.
According to NONA Composites president Ben Dietsch, the resin system’s cost is on par with other commercially available 250°F epoxies, while the mechanical properties are slightly better and the processing enables a lot of flexibility in both cure temp and time as well as tooling.
“This system was designed in response to feedback from our industrial and boatbuilding customers,” says Dietsch. “Our original NONA resin system, RT-177 (now R102/H11), had much higher temperature performance than they needed, which is a major driver for resin cost. So we developed a system that contained all the NONA processing benefits, but is tailored to meet the temperature, mechanical property and cost requirements of these markets.”
A key application of this new system will be in filament wound tanks for compressed natural gas (CNG) storage and other alternative energy markets. In order to measure the material’s performance beyond standard testing, NONA Composites worked with HyPerComp Engineering Inc. (Brigham City, UT, USA) to filament wind and burst test a small composite overwrapped pressure vessel. An aluminum liner overwrapped with T700 carbon fiber and NONA R404/H18 resin was cured using a 2-hr heat-added cure cycle at 250°F/120°C but without post-cure. (Heat was added due to the aluminum liner heat sink.) The vessel was then burst according to standard in-house HyPerComp Engineering procedures. The comparison of delivered fiber strength to that predicted by HyPerComp's computer finite element analysis (FEA) was 102%, demonstrating its successful performance in this standard test setup. The next step is to build and burst test the same tank using a 15-min heated cure, as NONA Composites continues working with HyPerComp Engineering to evaluate R404/H18 epoxy’s performance with fiberglass-based filament wound vessels.
In addition to the work in filament wound structures, NONA Composites is demonstrating its R404/H18 epoxy in a 500 ft2 infused hybrid fiberglass and carbon structure. The company will showcase this part production in 2016 as a demonstration of the ability to fabricate larger components more rapidly without an oven or added heat.
For more details on the new NONA R404/H18 resin, visit NONA Composites in the 2015 CAMX Exhibit Hall at booth M100. Ben Dietsch will also be presenting “Process and Property Characteristics of No-Oven, No-Autoclave Composite Part Production” on Wed, Oct. 28 from 2:30-2:55 in room D171. This presentation will walk through the composite processing and cured laminate property data from a major part fabrication program in 2014 (see "CFRP camera boom enables safe spill inspection") with the goal of giving composite manufacturers more information on what to expect with infusion, curing and production repeatability when using NONA no-oven no-autoclave resin systems.
Related Content
Plant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MoreJeep all-composite roof receivers achieve steel performance at low mass
Ultrashort carbon fiber/PPA replaces steel on rooftop brackets to hold Jeep soft tops, hardtops.
Read MoreWelding is not bonding
Discussion of the issues in our understanding of thermoplastic composite welded structures and certification of the latest materials and welding technologies for future airframes.
Read MoreOptimizing a thermoplastic composite helicopter door hinge
9T Labs used Additive Fusion Technology to iterate CFRTP designs, fully exploit continuous fiber printing and outperform stainless steel and black metal designs in failure load and weight.
Read MoreRead Next
CFRP camera boom enables safe spill inspection
NONA Composites’ 32m REACH structure meets tight remediation schedule at DoE radioactive waste storage site.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read More





















