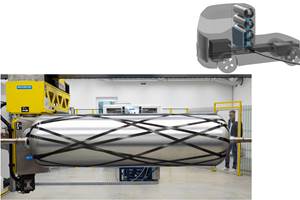
AMRC installing UK's largest radial braider
The new radial triaxial braider will support the development of complex lightweight preforms for automotive, aerospace and other weight sensitive industries.

Source | AMRC
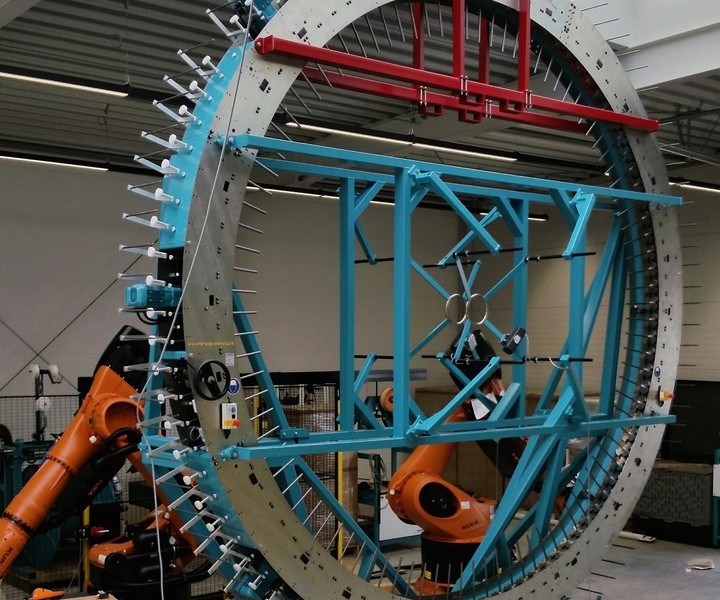
The largest radial triaxial braider in the UK is currently being installed at the University of Sheffield Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC, Sheffield, UK) to support the development of complex lightweight preforms for automotive, aerospace and other weight sensitive industries.
The equipment, which is supplied by Herzog GMBH (Oldenburg, Germany), is part of a collection of state-of-the-art equipment purchased by the AMRC with funding from the Aerospace Technology Institute (ATI, Bedford, UK).
The giant 6m diameter braiding system paves the way for the development of manufacturing complex architectures and features with dry fiber technology, offering the ability to tailor orientations to suit structural requirements as well as allowing both off axis and axial fibers to be laid simultaneously at the deposition rates required for high volume manufacture.
A wide range of materials can be used with the radial braider including carbon, thermoplastic, glass, aramid and co-mingled tows. The Braider is also capable of processing ceramic fiber such as alumina and silicon carbide which would otherwise be difficult to process on a conventional braiding machine.
It has widespread application for components used in aerospace and automotive, helping with the production of fuel pipes and wing spars and numerous car body structure parts. It will also be available to support Dowty Propeller’s (Staverton, UK) multimillion pound Digital Propulsion project to develop future turboprop solutions.
Chris McHugh, Dry Fiber Development Manager at the AMRC Composite Centre, explains,
“The radial element is a primary feature of the braider as it means less fiber damage and more complex geometry is achievable due to the fact the fibers come down in a flat disc rather than a long cone. The machine is also six-axis with two robots. Quite often one robot is attached to a braider but the AMRC are putting two heavy duty robots either side of the braiding ring. The two 6-axis robots working in tandem means heavy parts and mandrels can be processed and not just foam cores. It is also able to handle more delicate or less stiff cores, due to the additional support.”
The technology, which is open to research projects for AMRC members, external companies and grant funded projects, can be combined with any of the other technologies at the AMRC, including the 1000T Rhodes press and KraussMaffei (München, Germany) RTM equipment.
Consultant engineer at the AMRC Composite Centre, Andy Smith, says,
“The advantage is it can be combined with other dry fiber technology as AMRC have the full process chain to generate parts to demonstrate industrial scale, high volume production. The AMRC was considering one of these braiding machines over ten years ago when the Composite Centre was starting out, it is technology they have wanted for a long time but it didn’t suit the market at that time, which was focused more on prepeg rather than dry fiber. With the setup of this machine, the braider has the potential to process delicate ceramic fibers for metal or ceramic matrix composites which have higher temperature capabilities and higher stiffness - making them suitable for military applications.”
The braider’s arrival follows the delivery of a 3D weaving loom and Jacquard currently under construction at the Composite Centre. Other cutting edge equipment includes through-thickness permeability testing, tailored fiber placement, a high temperature-high tension filament winder, tow-spreading machine and robotic end effectors for automated handling.
It will be used not only to manufacture preforms but also to develop the enabling technology for commercialization including joining, automation and impregnation.
The AMRC Composite Centre is on the lookout for companies to work with on collaborative research and development projects using the braiding system. Contact Chris McHugh by emailing c.mchugh@amrc.co.uk.
Related Content
Infinite Composites: Type V tanks for space, hydrogen, automotive and more
After a decade of proving its linerless, weight-saving composite tanks with NASA and more than 30 aerospace companies, this CryoSphere pioneer is scaling for growth in commercial space and sustainable transportation on Earth.
Read MoreASCEND program update: Designing next-gen, high-rate auto and aerospace composites
GKN Aerospace, McLaren Automotive and U.K.-based partners share goals and progress aiming at high-rate, Industry 4.0-enabled, sustainable materials and processes.
Read MoreThe potential for thermoplastic composite nacelles
Collins Aerospace draws on global team, decades of experience to demonstrate large, curved AFP and welded structures for the next generation of aircraft.
Read MoreCryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreRead Next
Developing bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read More