B&T Composites joins R&D project to develop novel composite hydrogen storage tanks
As part of the Greece-based H2Cat project, the company says new tanks will be developed and studied with embedded structural health monitoring (SHM) sensors.
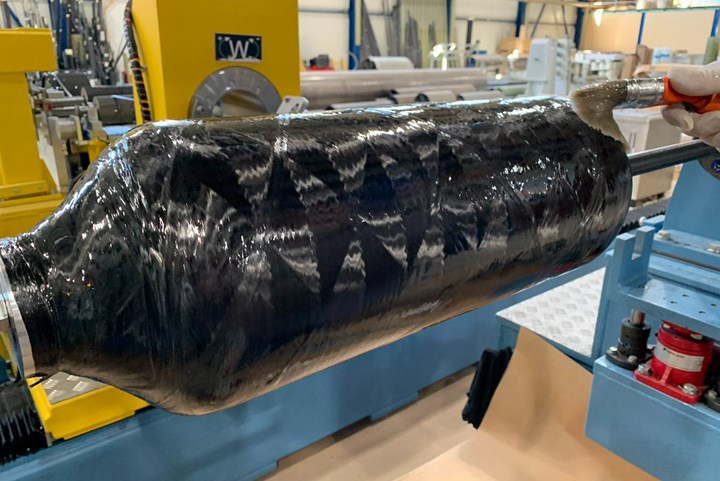

Photo Credit, all images: B&T Composites
B&T Composites (Florina, Greece) recently announced that it will be part of a new project focused on novel carbon fiber composite pressure vessels for hydrogen storage, to begin later this year.
As part of a European Union-backed IPCEI (Important Projects of Common European Interest) called H2CAT, B&T Composites seeks to develop novel pressurized hydrogen storage tank products that will eventually form a new market standard for stationary and transportation-related hydrogen storage. The company says this goal will be achieved by addressing major, well-documented issues with the current technology for pressurized hydrogen storage.
B&T Composites will develop the high-pressure hydrogen cylinders as well as the corresponding certification process according to the latest codes and standards. The company will be provided the technical specifications, requirements and objectives for the storage system integration and application by a consortium of companies and universities, brought together through the matchmaking process of IPCEI, while developing its own internal target specifications.
Academic partners include the Department of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Western Macedonia (Kozani, Greece), the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at the University of Ionnina (Ioannina, Greece), the Department of Electronic Engineering at Hellenic Mediterranean University (Iraklio, Greece) and the Centre for Research and Technology Hellas (CERTH) through the Chemical Process & Energy Resources Institute (CPERI).
“We are excited to participate as novel energy storage systems partners in this huge European project. It will push the transition to a greener economy so as to be in compliance with the demand for a hydrogen strategy for a climate-neutral Europe and the creation of a hydrogen market,” says Vasilis Tiriakidis, president and CEO of B&T Composites.
H2CAT belongs to the technical field 3 that is dedicated to technology storage and is said to include the following innovations:
- Cutting-edge composite manufacturing methods
- Advanced, carbon-based nanomaterials
- Optimization through computer design and simulation
- Extensive testing and quality control of the product
- Integrated monitoring system to improve safety
The project will include research and development (R&D) actions for both Type IV and V vessels, as well as innovation activities related to the construction of Type V storage vessels and the non-destructive evaluation of the stresses and the hydrogen permeability by integrating optical fibers in the structures. The new storage tanks will be designed using state-of-the art nanocomposite materials and modeling tools, with support from researchers at prominent academic institutions and research institutes in Greece that will contribute as subcontractors and a team of dedicated consulting engineers at B&T.
An optical fiber-based NDI system for measuring the mechanical stresses and hydrogen permeability will also be integrated in the composite shell of the tank, to continuously monitor its performance during its life cycle. The final tank designs will be tested and verified through laboratory measurements at certified facilities.
Focus on photonics-based structural health monitoring (SHM)
In addition, as part of the project B&T Composites will integrate structural health monitoring (SHM) technology into the Type IV hydrogen storage tanks that are developed, aiming to efficiently address typical safety issues with hydrogen tanks.

B&T says it will employ both mature technologies such as Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBGs) as well as novel optical fiber designs and sensor layouts. The company says that the major advantage of using optical fiber sensors (learn more, “Sensors: Data for next-gen composites manufacturing”) is their small footprint and structural compatibility — in other words, their ease of integration inside the carbon fiber structure, with minimal perturbation of the surrounding carbon fiber layup. This compatibility is said to hold true, especially for small-diameter optical fiber, namely optical fibers with a diameter of 50 micrometers, or half the diameter of typical human hair. Therefore, B&T aims at the installation of various optical fiber sensors inside the hydrogen tanks, while retaining excellent structural rigidity provided by the carbon fiber superstructure.
One of the sensing technologies to be embedded in the hydrogen tanks are Fiber Bragg Gratings. FBGs are manufactured by laterally exposing the core of a single-mode fiber to a periodic pattern of intense laser light. The exposure produces a permanent increase in the refractive index of the fiber’s core, creating a fixed index modulation according to the exposure pattern. This fixed index modulation is called a grating. The ability to accurately preset and maintain the grating wavelength is a fundamental feature and advantage of fiber Bragg gratings.
The central wavelength of the reflected component satisfies the Bragg relation: λBragg = 2nΛ, with n the index of refraction and Λ the period of the grating. Due to the temperature and strain dependence of the parameters n and Λ, the wavelength of the reflected component will also change as function of temperature and/or strain. Thus, another major advantage of using FBGs is the fact that sensing information is wavelength encoded, an invaluable asset when working in environments prone to intensity losses, B&T Composites says.
In order to successfully integrate these sensors inside the hydrogen tanks, B&T will develop novel manufacturing approaches both for the in- and out- coupling, as well as for the embedding of the small diameter optical fibers and unique encapsulation technologies.
In addition, B&T looks to further innovate in the photonic sensing front. Within the frame of the H2CAT project, novel optical fiber-based hydrogen sensors will be developed and deployed at different radial positions of the tank walls. These novel sensors will be able to measure hydrogen diffusion (if any) and provide an early warning system for possible maintenance actions, enhancing the service lifetime and safety of the pressurized tank vessels.
These sensors will work in conjunction with the standard small diameter optical fiber FBGs and provide a holistic, multi-parameter sensing approach in the structural health monitoring of these tanks. Within one optical fiber cable, temperature, strains, pressure, hydrogen diffusion and acoustic emission monitoring will take place providing the end user with all the data needed to assess the health status of the vessel under investigation.
The project is expected to start by the end of 2022 and the overall timeline of the project will be divided in four stages: RDI stage I & II, FID stage I & II.
Related Content
Hexagon Purus opens new U.S. facility to manufacture composite hydrogen tanks
CW attends the opening of Westminster, Maryland, site and shares the company’s history, vision and leading role in H2 storage systems.
Read MoreMidnight production aircraft completes full transition flight
This is Archer’s second full-scale eVTOL aircraft to achieve this milestone, critical to being able to carry commercially viable passenger payloads.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Automotive (2024)
Recent trends in automotive composites include new materials and developments for battery electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cell technologies, and recycled and bio-based materials.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Pressure vessels (2024)
The market for pressure vessels used to store zero-emission fuels is rapidly growing, with ongoing developments and commercialization of Type 3, 4 and 5 tanks.
Read MoreRead Next
Hydrogen is poised to fuel composites growth, Part 1
Applications abound for composite tanks to store compressed H2 gas, but challenges exist in cost, size, efficiency and limited carbon fiber capacity.
Read MoreHydrogen is poised to fuel composites growth, Part 2
Potential for Type IV composite tanks in H2 refueling stations and distribution, plus targeted cost reductions and emerging technologies for tank recertification and monitoring.
Read MoreSensors: Data for next-gen composites manufacturing
In the quest for sustainability, sensors are reducing cycle times, energy use and waste, automating closed-loop process control and increasing knowledge to open new possibilities for intelligent manufacturing and structures.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)