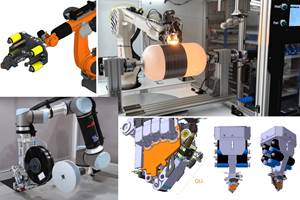
Coriolis introduces hybrid CPico AFP machine
This compact cell brings together 3D printing, AFP and milling aided by a comprehensive software program, further simplifying the manufacture of complex thermoplastic composite aerostructures in the future.

The hybrid CPico system. Photo Credit, all images: Coriolis Composites
Coriolis Composites (Quéven, France) has been designing and providing automated fiber placement (AFP) cells for the aerospace industry for more than two decades. For the last couple of years, Coriolis says it has pushed the boundaries of compact end effectors dedicated to the manufacture of complex parts, highlighted in the recently released CPico system.
The Coriolis CPico is a compact cell combining two different manufacturing technologies: AFP and additive manufacturing (AM). AFP brings high performance through the use of continuous carbon fiber while the system’s AM-related features bring complexity and functionalities into the part. CPico also enables the use of thermoplastic composites — for toughness, recyclability, repairability and temperature resistance — which is in line with recent developments in materials for aerospace.
CPico is made possible through the use of a Siemens-controlled six-axis robot combined with a two-axis positioner. The use of multiple axes enables true 3D trajectories and optimized robot postures for improved manufacturability, Coriolis notes. Four different processes are available on the cell and processes are swapped from one to the other thanks to an automatic toolchanger — these include two AM processes, fused filament fabrication (FFF) and fused granular fabrication (FGF), with AFP and potentially milling in the future. The heads are designed to process high-temperature polymers (PAEK family) at room temperature with in-situ consolidation standards (less than 1% porosity, high ILSS and crystallinity).
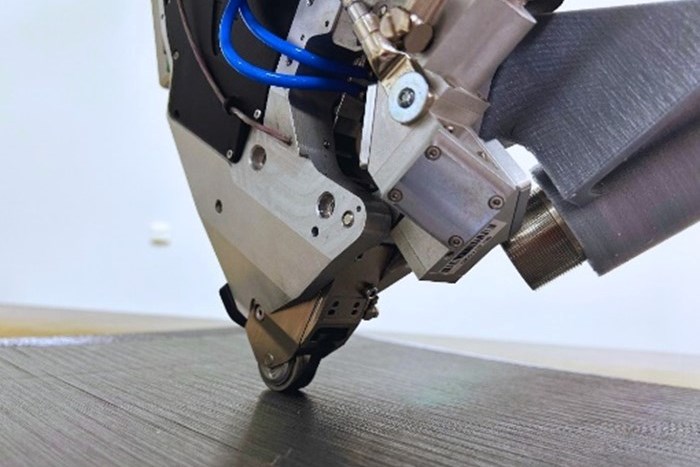
CPico AFP head.
The system’s AFP end effector is a compact, single-tape tool that can process several fiber widths ranging from 1 mm or 6.35 mm ( ¼"). While ¼" tows are used to make panels comparable to bigger machines (the Coriolis C1.2, for instance), 1-mm tows allow the user to make use of the potential of anisotropic carbon fiber and are used to provide localized and highly oriented additional reinforcement. From a manufacturing point of view, it can also achieve very tight steering radii. Moreover, a fiber tensioning device has been added to the head for certain applications such as filament winding.
The FFF and FGF end effectors have been designed with the same philosophy: providing in-situ consolidation with good adhesion and near-zero porosity. To do so, specific extrusion dies have been designed (ranging from 0.4-1.2 mm in diameter) to create polymer matrix flow. Moreover, localized heating is used to favorize molecular mobility for optimized adhesion between layers. The FGF end effector, while more complex than the FFF, is also reported to be higher performing; its high wear resistance makes it capable of processing carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK compounds with high fiber volume fraction (up to 35%). An automatic die-cleaning and tool center point measurement device is also provided in order to obtain flawless prints.
AM prints are usually not suitable for net-shape parts and need post-treatment with a milling machine to reach its required accurate geometry. To eliminate moving the part from additive to subtractive cells, a milling tool is embedded into the solution (expected 2024). This tool will be developed by robotic milling solutions supplier Creno (Annecy, France). It’s able to perform trimming, drilling and surfacing operations and incorporates a vacuum unit for switching between processes without intermediate cleaning.
Moreover, to generate a single program for the different manufacturing processes, a dedicated path-planning CAM software has been developed:
- Advanced slicer engine for planar, multi-planar and curved (non-planar) slicing of geometries (mesh and parametric/exact shapes).
- Path-planner: Hybrid continuous fiber reinforcement (based on Coriolis’ knowledge of fiber placement path programming) and filament/pellet extrusion path generation (such as single-stroke continuous extrusion path planning). It also includes filament winding planning and machining operations planning, with manual path waypoints edition for local adjustments.
- Advanced motion planner for complex, robot-based kinematics programming and simulation with external devices (such as dual-axis rotational table/positioner), including collision-avoidance and toolpath smoothing optimization.
- NC-code machine simulation: A digital twin of the robotic machine, based on the Siemens NC Virtual Controller (Sinumerik Run My-VNCK and S-One), including collision detection and realistic material deposition simulation.
CPico has been developed to manufacture complex, multi-functional thermoplastic composite parts where conventional process are not suitable. It also aims to eliminate the need for additional manufacturing cells, such as welding. Application examples include filament-wound tanks, composite sandwich structures, hybrid AFP/AM parts with fixation devices and more. Several research projects funded by the European Union incorporating CPico are ongoing with aerospace Tier 1 suppliers.
Related Content
Plant tour: Albany Engineered Composites, Rochester, N.H., U.S.
Efficient, high-quality, well-controlled composites manufacturing at volume is the mantra for this 3D weaving specialist.
Read MorePlant tour: Spirit AeroSystems, Belfast, Northern Ireland, U.K.
Purpose-built facility employs resin transfer infusion (RTI) and assembly technology to manufacture today’s composite A220 wings, and prepares for future new programs and production ramp-ups.
Read MoreThe next evolution in AFP
Automated fiber placement develops into more compact, flexible, modular and digitized systems with multi-material and process capabilities.
Read MoreJeep all-composite roof receivers achieve steel performance at low mass
Ultrashort carbon fiber/PPA replaces steel on rooftop brackets to hold Jeep soft tops, hardtops.
Read MoreRead Next
Coriolis highlights C1.2 compact AFP system for multi-material applications
New developments regarding productivity, maintenance and ergonomics make this enhanced composite placement system well suited for the production of complex parts.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More