Center for mass production of lightweight composites
German R&D center brings together 8 institutes and more than 80 companies from 120 countries to help industrialize composite parts production.
The Aachen Center for Integrative Lightweight Production (Achener Zentrum für integrativen Leichtbau, or AZL) of RWTH Aachen University (Aachen, Germany) was established in 2012 with the mission to develop breakthrough technologies for the mass production of lightweight composite parts.
AZL comprises two separate entities:
AZL of RWTH Aachen University conducts research and development in lightweight products, materials, production processes and systems with access to the latest full-scale machines and automation systems.
AZL Aachen GmbH provides industrial services in engineering, consultancy and project management, networking and business development, enabling close cooperation between the lightweight industry and the research institutes of RWTH Aachen Campus along the whole value chain.
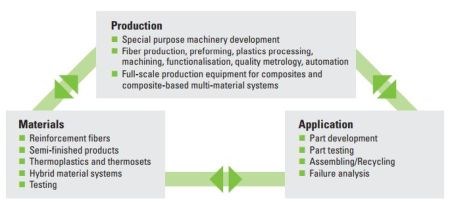
According to AZL, composites have a tremendous potential but they require an integrative and interdisciplinary approach along the entire value chain. Thus, AZL brings together 8 institutes which cover the entire value chain for composites. Its goal is to bring together materials science and production technology in order to generate efficient process chains for industrialized production.

|
AZL’s integrative approach to industrialization of composite and multi-material parts production. SOURCE: AZL digital booklet.
AZL has ongoing projects and partnerships in the following business segments/industries:
- Automotive and Transportation
- Aerospace
- Energy Engineering
- Oil & Gas/Process Engineering
- Machinery and Plant Engineering
- Consumer, Sports, Leisure
- Building and Construction
For building and construction, it has started a joint market and technology study, in partnership with AVK, Federation of Reinforced Plastics e.V. (Frankfurt, Germany).
AZL is also supporting what it calls Business Platforms, including websites that provide industrial players — especially OEMs and Tiers — with details on lightweight technologies:


|

|

|

|
These correspond to AZL's four main Industrial Workgroups, which meet every six months. AZL also has conducted the following Exemplary Workshops to tackle targeted issues:
- Joining
- Design and Process Systematics
- Process Costing
- Research Landscape for Composites.
SOURCE: AZL partnership brochure.
In a related initiative, AZL partners have decided on a new collaborative model — called Joint Business Development — to pursue new markets and regions for business development, supported by co-working spaces on the RWTH Aachen campus.
2017 AZL Partners Meeting
AZL has developed a network of more than 80 companies from 21 different countries. SOURCE: AZL.
AZL has built an international partner network comprising its 8 collaborative institutes and more than 80 companies involved in lightweight production. The 2017 annual AZL partner meeting was held on June 27-28, and comprised meetings of the four industrial workgroups as well as meetings of four ongoing Joint Partner Projects, which are jointly funded pre-competitive research and development initiatives:
- New Designs for Low-Cost and Energy-Efficient Double-Belt Presses
- Thermoplastic Tapes – Material and Processing Benchmark
- Ultra-Fast Manufacturing of Tailored Composite Blanks
- End-machining of Fiber-Reinforced Plastics
Discussion of Mobility and Transportation
During the 2017 meeting, AZL partners discussed upcoming market trends and barriers in a workshop session. Mobility and transportation were identified as the most important markets for lightweight technology. Future mobility concepts including autonomous driving and electric mobility will have a large impact on lightweight products, technologies and materials according to the participants’ discussion.
Dr. Thierry Renault, manager of Partnerships for Composite Technologies at Faurecia Clean Mobility, and keynote presenter at the meeting states:
“Our aim is to become a global leader for supplying composite parts for the highly cost-driven automotive industry. We regard cost-neutral weight reduction and the provision of efficient engineering tools as the key challenges for composites in automotive mass production. Composite players need to act and cooperate on all levels in the composite value chain in order to compete with fast developing alternative technologies.”

|

|
The eGO Life.
SOURCE: www.e-go-mobile.com
The RWTH spin-off e.GO Mobile AG presented the e.Go Life, an electric car which was developed in a 3-year process on the RWTH Aachen Campus. The ramp-up of serial production in spring 2018 is the starting point for projected production capacities of 10,000 cars per year.
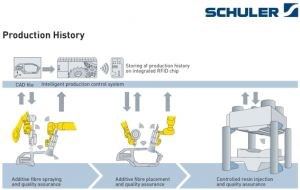
Other presentations included the Laboratory for Machine Tools and Production Engineering (WZL) of RWTH Aachen University, which showed quality assurance equipment and research results for composite systems. Schuler (Göppingen, Germany) presented its 1,800-ton composite press which is currently integrated into a self-regulating production system within the iComposite 4.0 project, funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF).
(Note: Schuler recently installed a similar press in the IACMI facility operated by Michigan State University in Detroit.)
|

|
Schuler leads the iComposite 4.0 project which aims to achieve cost savings by producing near net shape parts using additive fiber spraying to create preforms, automated resin injection (HP-RTM) and an IIoT-networked intelligent production system which includes storing the production history on an RFID chip integrated into the part. SOURCE: Schuler.
AZL also presented the manufacturing of hybrid parts, consisting of continuous carbon fiber thermosets overmolded with thermoplastic stiffening structures.
Dr. Hartmut Saljé, head of Corporate Engineering at Mubea (see blog “Mubea Carbo Tech: High-quality auto composites go high-volume”) presented a broad range of lightweight components for automotive applications and introduced the Mubea Centre for Lightweight Design in the Production Engineering Cluster on the RWTH Aachen Campus:
“At Mubea and our subsidiary Carbo Tech, we produce innovative and efficient lightweight products and work on e-mobility solutions. In the past, our co-developments together with RWTH Aachen have contributed a lot to our technological leadership in order to keep track on the fast development for automotive applications. This is why we situated our Centre for Lightweight Design in the Production Engineering Cluster on the RWTH Aachen Campus to collaborate with innovative companies and institutes on site on our metal- and composite-based lightweight solutions.”
Related Content
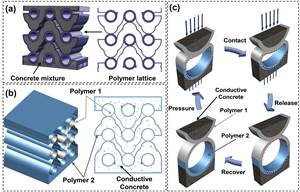
21st century concrete: composite metamaterial with super compressability, energy harvesting
Material comprising 3D-printed, auxetic, reinforced polymer lattices in conductive cement matrix can compress up to 15% and generate electricity for lightweight, mechanically tunable structures with energy harvesting and sensing.
Read MoreGatorbar, NEG, ExxonMobil join forces for composite rebar
ExxonMobil’s Materia Proxima polyolefin thermoset resin systems and glass fiber from NEG-US is used to produce GatorBar, an industry-leading, glass fiber-reinforced composite rebar (GFRP).
Read MoreComposites end markets: Infrastructure and construction (2024)
Composites are increasingly used in applications like building facades, bridges, utility poles, wastewater treatment pipes, repair solutions and more.
Read MoreComposites-reinforced concrete for sustainable data center construction
Metromont’s C-GRID-reinforced insulated precast concrete’s high strength, durability, light weight and ease of installation improve data center performance, construction time and sustainability.
Read MoreRead Next
Plant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More