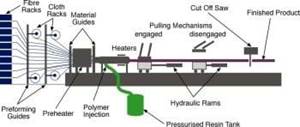
Huntsman Advanced Materials resin systems meet composite pressure vessel requirements
Araldite resin systems cover wet and towpreg filament winding and RTM manufacturing processes for increased productivity and greater part consistency.
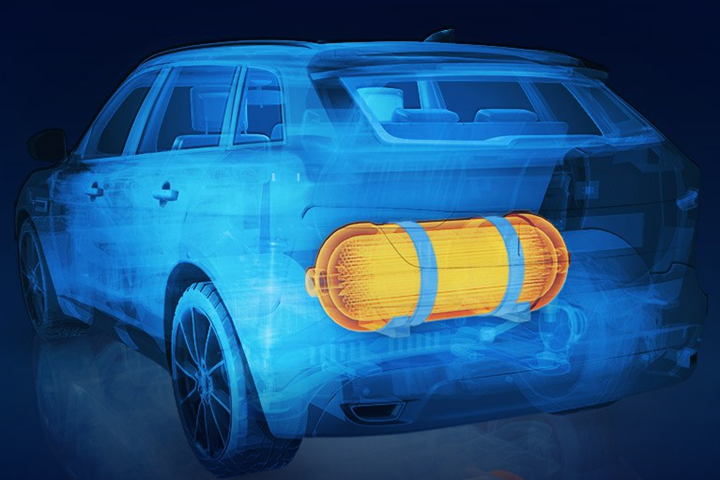

Photo Credit: Huntsman Corporation
According to Huntsman Advanced Materials (The Woodlands, Texas, U.S.), as hydrogen roadmaps and investments grow and enter new applications, hydrogen storage in pressure vessels will become a critical enabler for wide-scale adoption and the subject of intensive research and development. To further this progress, the company has developed the Araldite range for filament-wound composite pressure vessels. Encompassing high-performance epoxy, acrylic, polyurethane adhesives, high-performance specialty epoxy and benzoxazine resin systems, Araldite is said to be able to meet the stringent requirements for hydrogen storage. This includes pressure testing, impact resistance, chemical exposure and other temperature and pressure cycling tests and regulations.
According to Huntsman, while the pressure resistance of hydrogen vessels is mainly governed by the fiber reinforcement, the resin matrix plays a key role in providing environmental exposure protection (thermal, chemical, impact) as well as fatigue/pressure-cycling resistance to withstand the filling and emptying cycles. Table 1 below shows three examples of high-performance epoxy-based systems that offer a combination of thermal resistance, high mechanical strength, high elongation at break and high fracture toughness.
|
Resin system |
Araldite resin / |
Araldite resin / |
Araldite LY3508 / Aradur 3478 |
|
Process |
Wet filament winding |
Towpreg filament winding |
RTM |
|
Cure cycle |
2 hours, 80°C + 2 hours, 110°C |
30 min, 140°C |
20 min, 100°C + 2 hours, 130°C |
|
Tg (°C) DSC midpoint, ISO |
120 |
132 |
115 |
|
Tensile strength (MPa) ISO 527 |
75 |
77 |
70 |
|
Fracture toughness KIc (MPa.m1/2) ISO 13586 |
1.58 |
1.55 |
1.7 |
In addition, Araldite solutions for pressure vessels cover a range of manufacturing processes: wet filament winding is a well-established manufacturing method, but increasingly resin transfer molding (RTM) and towpreg winding are considered in order to meet the need for increased productivity and greater part consistency.
Huntsman Advanced Manufacturing further identifies the process features for each method, which offer a range of options for composite pressure vessel manufacturing. For example, wet filament winding is a well-established process, which offers winding speeds of 1-2 meters per second at maximum and a range of winding angles. Towpreg filament winding is a clean process, with fast winding speeds of >5 meters per second, with controlled and consistent resin content, variable winding speed (fast on hoops, slower on domes), a range of winding angles and optimized winding patterns. The process also enables high reproducibility and short cure times (down to 30 minutes). Alternately, the RTM process enables fast injection versus filament winding operations, fast cure in the mold (20 minutes), and is ideal for small-sized vessels. RTM also ensures high laminate quality (low porosity content), high investment (braiding, molds, press, dosing equipment) and higher resin content than towpreg and filament winding.
Building on a strong experience in natural gas pressure vessel technology, Huntsman Advanced Materials adds that it can offer a comprehensive range of epoxy resin systems that address the emerging challenges and manufacturing requirements for hydrogen storage. In addition, expertise in material characterization and process simulation offer a powerful tool to accelerate product development and optimize manufacturing, leading to increased part quality and minimum production cycle times.
This post is courtesy of the CompositesWorld and AZL Aachen GmbH media partnership.
Related Content
Jeep all-composite roof receivers achieve steel performance at low mass
Ultrashort carbon fiber/PPA replaces steel on rooftop brackets to hold Jeep soft tops, hardtops.
Read MorePultrusion: The basics
A primer describing what pultrusion is, its advantages and disadvantages, and typical applications.
Read MoreActive core molding: A new way to make composite parts
Koridion expandable material is combined with induction-heated molds to make high-quality, complex-shaped parts in minutes with 40% less material and 90% less energy, unlocking new possibilities in design and production.
Read MoreThe next evolution in AFP
Automated fiber placement develops into more compact, flexible, modular and digitized systems with multi-material and process capabilities.
Read MoreRead Next
Huntsman PU resin systems enable lightweight sandwich construction for automotive
Vitrox RTM and Rimline FC polyurethane systems to advance lightweighting, design freedom and simplified manufacturing opportunities.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read More